
The 2026 AI Bot Impact Report: What It Means for Shared Web Hosting
TL;DR
- AI bots now dominate web traffic, overwhelming shared hosting resources and pushing many sites toward VPS or isolated hosting for stability and performance.
- AI bots generate 52% of global traffic and up to 70% of dynamic resource usage, creating CPU, RAM, and bandwidth pressure beyond what shared hosting was built to handle.
- Growth is driven by AI search engines, LLM agents, and scrapers that frequently recrawl pages, execute JavaScript, and hit deep archives without adding real human visitors.
- On shared hosting, the “noisy neighbor” effect means heavy bot activity on other accounts can slow or crash your site even when your own human traffic is low.
- AI bot load can hurt SEO by consuming crawl budget, slowing responses, degrading Core Web Vitals, and delaying indexing of new content.
- Effective mitigation includes WAF rules, rate limiting, CDNs, and often upgrading from shared hosting to VPS or isolated environments to regain resource control.
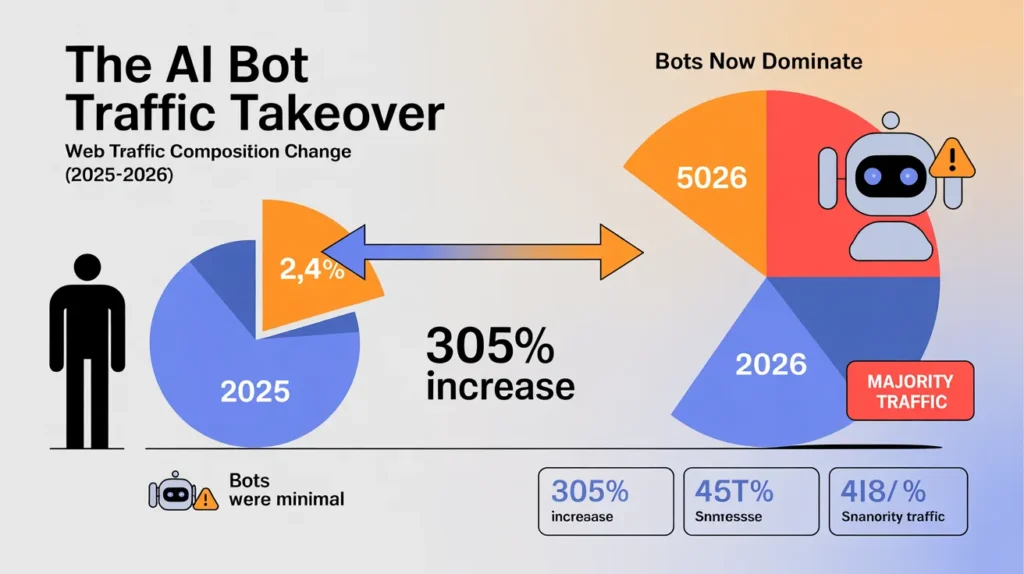
The internet has fundamentally changed, and for website owners on shared hosting plans, the ground is shifting beneath their feet. According to the 2026 AI Bot Impact Report, bots now account for 52% of all global web traffic, outnumbering human visitors by approximately three to one. This isn’t just a vanity metric—it is a resource crisis.
For years, shared hosting was the economical, logical choice for small to medium-sized websites. It relied on a simple premise: not every website needs maximum server power all the time.
However, the explosive rise of AI crawlers, large language model (LLM) agents, and data scrapers has broken that model. These bots do not browse like humans; they consume, extract, and execute code at a scale that shared servers were never designed to handle.
If your website has been experiencing unexplained slowdowns, bandwidth throttling, or inaccurate analytics, you are likely feeling the effects of this new bot-dominated landscape. This guide breaks down exactly how AI bots affect shared environments and why the traditional hosting model is struggling to keep up.
Why AI Bots Are Increasing Rapidly in 2026
The surge in bot traffic is not accidental. It is the direct result of an arms race in the artificial intelligence sector, where data is the most valuable currency. To train smarter models, companies must harvest more data, more frequently.
Rise of AI search engines and agents
We have moved past the era where Google was the only major crawler that mattered. New AI-powered search engines and answer engines—like Perplexity, SearchGPT, and others—require constant, real-time access to web content to function.
Unlike traditional search engines that index a page once every few days, AI agents often return to verify facts or pull fresh data for real-time user queries. This multiplies the number of visits a site receives without necessarily increasing the number of human eyes on the content.
How GPTs, crawlers, and AI assistants access websites
The 2026 report indicates that AI and LLM crawlers quadrupled their traffic share from 2.6% to 10.1% in just eight months. OpenAI’s GPTBot alone grew by 305%.
These assistants access websites to summarize content for users, check stock availability, or aggregate news. While this can drive visibility, it places a heavy load on the hosting infrastructure, as these bots often ignore standard caching protocols to ensure they get the “freshest” version of a page.
Difference between traditional bots and AI bots
Traditional search crawlers were relatively polite. They fetched the HTML, indexed the text, and left. Modern AI bots are different. They simulate human user actions.
They execute complex JavaScript, interact with dynamic elements, and follow deep links to extract training data. This “user action” crawling increased 15x in 2025. For a server, serving a static HTML file is easy; executing JavaScript for a bot is significantly more resource-intensive.
What Are AI Bots and How Do They Interact With Websites?
Understanding the nature of these bots is the first step toward mitigating their impact. They are not malicious in the sense of a DDoS attack, but their behavior can be just as damaging to server stability.
Types of AI bots and crawlers
Not all bots are created equal. The landscape is currently dominated by Meta, whose crawlers account for 52% of AI bot traffic, followed by Googlebot (23%) and OpenAI (20%).
- Training Crawlers: These scour the entire web to build datasets for future models. They are voracious and thorough.
- Real-Time Agents: These act on behalf of a user to fetch immediate answers.
- Commercial Scrapers: These harvest pricing, inventory, or content data for competitors or aggregators.
How AI bots consume server resources
Bots are responsible for up to 70% of dynamic resource consumption on web servers. When a human visits a site, they might load a page, read for two minutes, and then click a link. A bot might hit 50 pages in two seconds.
If your website relies on a database (like WordPress), every one of those hits triggers a database query. On a shared server, thousands of database queries in a short window can lock up the CPU, causing the “Error establishing a database connection” message that strikes fear into the hearts of site owners.
Request patterns compared to human users
Human traffic usually follows predictable patterns: it rises during the day and falls at night. Bot traffic is relentless and erratic. It can spike at 3:00 AM just as easily as 3:00 PM.
Furthermore, humans rarely check old archive pages from five years ago. AI bots do. They dig deep into site architectures, forcing the server to retrieve un-cached, rarely accessed content, which requires more processing power than serving the popular, cached homepage.
How AI Bot Traffic Impacts Shared Web Hosting
Shared hosting operates on a communal model. Hundreds of accounts reside on a single server, sharing the same pool of CPU, RAM, and disk I/O. This architecture is the most vulnerable to the current wave of AI traffic.
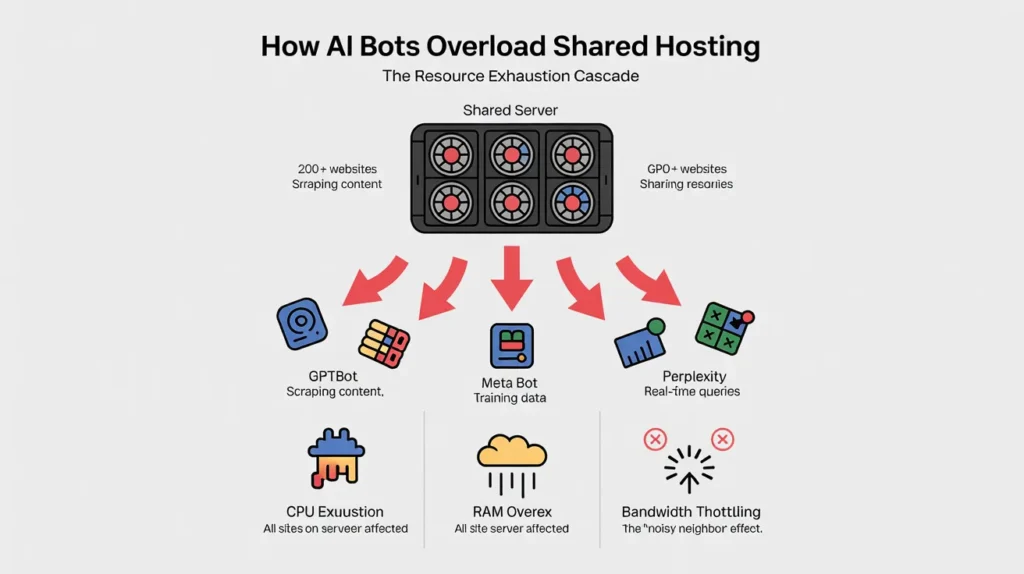
CPU and RAM exhaustion on shared servers
When an AI crawler hits a website on a shared server, it consumes a slice of that server’s processing power. If five websites on that server are being crawled simultaneously by Meta’s bot, the CPU usage hits a ceiling.
The server cannot distinguish between a “good” request and a “bad” one; it simply tries to process everything. Once the RAM is exhausted, the server starts swapping memory to the disk, which drastically slows down performance for every single website hosted on that machine.
Bandwidth overuse and throttling
Most shared hosting plans come with “unlimited” bandwidth, but this is often a marketing term subject to fair use policies. When AI bots scrape your site, they download images, scripts, and heavy media files repeatedly.
The 2026 report highlights that organizations blocking AI crawlers saw a 75% reduction in traffic and significant cost savings. For a shared hosting user, this invisible bot traffic can trigger bandwidth caps, leading to overage charges or temporary site suspension.
Increased latency and slow page loads
The “noisy neighbor” effect is the defining characteristic of shared hosting in the AI era. Even if your website has zero traffic, your page load speeds can plummet because another site on the same server is being aggressively scraped by PerplexityBot or GPTBot.
The queue for the server’s attention gets too long, and your human visitors are left waiting. Latency kills conversion rates, and on shared hosting, you have very little control over correcting it.
Why Shared Hosting Is Most Vulnerable to AI Traffic
The structural limitations of shared hosting make it ill-equipped for a web where bots outnumber humans.
Resource sharing limitations
In a shared environment, there is rarely a hard partition between users. Resources are pooled to keep costs low. This works when traffic is light and predictable. It fails when traffic is heavy and automated. A spike in demand from AI bots does not just slow down the target; it degrades the performance of the entire ecosystem.
Lack of isolation between accounts
Unlike a VPS (Virtual Private Server), shared hosting offers minimal isolation. If a neighboring account has a security vulnerability that attracts bad bots, or high-value content that attracts AI scrapers, your site suffers the collateral damage. You are effectively tethered to the traffic profiles of strangers.
Fair usage policies and hidden restrictions
Hosting providers manage shared servers by enforcing strict usage limits, often buried in the Terms of Service. If AI bots push your CPU usage above a certain percentage for too long, the host may automatically throttle your site or take it offline to protect the other users. You might be penalized for traffic you didn’t ask for and didn’t generate.
What Real Hosting Metrics Show About AI Bot Load
The data is clear: the behavior of server loads has changed.
Traffic spikes and crawl frequency
Server logs now show distinct “walls” of traffic. Instead of a gradual curve, resource usage spikes vertically when a major LLM updates its training data. These spikes are sharp, intense, and often brief, but they are powerful enough to crash a shared hosting process.
Server logs and bot behavior patterns
Analyzing server logs reveals that bots often ignore the “crawl-delay” directives in robots.txt files. They brute-force their way through sitemaps. The 2026 report notes that because 71.5% of traffic is bots, analytics data is systematically corrupted. Site owners might see a surge in “direct traffic” and assume their marketing is working, when in reality, it is simply a crawler scraping their content.
Early warning signs hosting users ignore
Many users dismiss brief periods of downtime or sluggishness as “internet hiccups.” In reality, these are often micro-outages caused by resource exhaustion. If your hosting dashboard shows high CPU usage during hours when your human audience is asleep, it is a red flag that AI bots are feasting on your server resources.
How AI Bots Affect SEO, Indexing, and Rankings
The impact of AI bots extends beyond server performance; it directly threatens your visibility on Google.
Crawl budget consumption
Search engines assign a “crawl budget” to every website—a limit on how many pages they will crawl in a given timeframe. If aggressive AI scrapers and third-party bots consume your server’s bandwidth and connection limits, Googlebot may not be able to crawl your site efficiently. It may interpret the slow server response as a sign of poor quality and crawl your site less frequently.
Impact on page indexing speed
If Googlebot cannot crawl your new content because the server is busy serving requests to an AI data harvester, your new pages will take longer to appear in search results. In news or e-commerce, where freshness is vital, this delay translates directly to lost revenue.
Performance signals and ranking risks
Google’s Core Web Vitals are a ranking factor. They measure speed, responsiveness, and visual stability. If AI bot traffic causes your server to lag, your Core Web Vitals scores will drop.
You could lose organic ranking positions not because your content is bad, but because your shared hosting environment cannot serve the content fast enough under the pressure of bot traffic.
What Website Owners Can Do to Reduce AI Bot Damage
While you cannot stop the AI revolution, you can take steps to shield your site.
Robots.txt and crawl control strategies
The first line of defense is your robots.txt file. You can explicitly disallow known AI bots like GPTBot, CCBot, and FacebookBot. However, this is a game of whack-a-mole; new bots appear weekly. Furthermore, not all bots respect these rules.
Rate limiting and firewall rules
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is essential. It can detect and block traffic that looks automated. Rate limiting allows you to set a cap—for example, “no more than 10 requests per minute from a single IP address.” This allows human users to browse normally while blocking bots that try to scrape hundreds of pages instantly.
Caching and CDN optimization
Offloading traffic to a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is one of the most effective strategies. A CDN serves cached versions of your pages from servers around the world. If a bot hits your site, the CDN serves the page, and your actual hosting server stays asleep. Aggressive caching prevents the database queries that usually crash shared hosting accounts.
When Shared Hosting Is No Longer Enough
There comes a point where optimizing a shared plan provides diminishing returns.
Signs it’s time to upgrade hosting
If your site goes down multiple times a week, if you are constantly hitting resource limits, or if your page load times are inconsistent, shared hosting is no longer viable.
If your business relies on web traffic for revenue, the “cost” of cheap hosting is actually the revenue lost during downtime—estimated globally at $204.8 billion in lost opportunity.
Performance thresholds to monitor
Watch your “Time to First Byte” (TTFB). If it consistently exceeds 600ms, your server is struggling. Monitor your “Wait” time in network requests. If the server takes seconds just to start sending data, it is overloaded.
Cost vs risk comparison
The jump from shared hosting to a VPS might cost an extra $10-$20 per month. However, the cost of a single hour of downtime during a sales event or a marketing campaign can be hundreds or thousands of dollars. In the AI era, reliability is a premium asset.
Why VPS and Isolated Hosting Are AI-Ready Solutions
Virtual Private Servers (VPS) and isolated hosting environments are the architectural answer to the AI bot problem.
Dedicated resources and isolation
On a VPS, your resources are yours. You are allocated a specific amount of RAM and CPU cores. If a neighbor on the physical hardware gets hit by a bot storm, your slice of the server remains unaffected. This isolation eliminates the “noisy neighbor” risk completely.
Better control over bot traffic
Root access on a VPS allows you to implement server-level blocking. You can install custom firewall modules, configure strict rate limiting at the web server level (Nginx/Apache), and ban entire IP ranges that are known for abusive bot behavior. You cannot do this on shared hosting.
Scalability for unpredictable AI loads
If AI traffic suddenly doubles, a VPS can often be scaled up instantly. You can add more RAM or CPU power with a click, allowing you to absorb the spike without crashing. Shared hosting is rigid; VPS hosting is elastic.
How Hosting Providers Must Adapt for AI Traffic in 2026
The hosting industry itself is undergoing a transformation to survive the 52% bot traffic reality.
Smarter traffic management
Providers are moving away from simple IP blocking and toward behavioral analysis. They are using AI to fight AI—deploying machine learning models at the network edge to identify bot signatures in real-time and divert them away from legitimate user traffic.
AI-aware hosting infrastructure
Hardware is changing. Servers now require faster disk I/O (like NVMe) to handle the database-heavy requests of modern bots. Network backbones are being upgraded to handle the massive bandwidth throughput required by training crawlers.
Security and bot classification
Hosts are beginning to offer “Bot Management” as a standard feature, rather than a premium add-on. Classifying traffic into “Good Bots” (Google), “Bad Bots” (scrapers), and “AI Crawlers” helps customers decide who gets let in and who gets blocked.
Why Skynethosting.net Is Prepared for the AI Hosting Era
For website owners looking to future-proof their digital presence against the rising tide of AI traffic, Skynethosting.net offers an infrastructure built for resilience.
AI-friendly VPS and hosting architecture
Skynethosting.net utilizes NVMe storage, which is 900% faster than traditional SATA drives and 200% faster than standard SSDs. This speed is critical for handling the database queries triggered by AI crawlers. Combined with LiteSpeed Web Server technology, which handles high-concurrency connections significantly better than Apache, Skynethosting.net servers are designed to remain stable even during traffic spikes.
Resource isolation and scalability
Understanding the risks of the “noisy neighbor” effect, Skynethosting.net provides robust VPS and dedicated server options that guarantee resource isolation. Their infrastructure allows businesses to scale effortlessly, ensuring that a sudden influx of AI agent traffic results in a served page, not a server crash.
Expert support for performance tuning
Navigating bot mitigation can be complex. Skynethosting.net offers 24/7 expert support to assist with configuration. Whether it is tuning LiteSpeed Cache for WordPress to minimize server load or setting up server-level rules to filter aggressive crawlers, their team acts as a partner in maintaining site performance.
Conclusion
The 2026 AI Bot Impact Report serves as a wake-up call for the web hosting industry and website owners alike. With bots now comprising the majority of internet traffic, the traditional shared hosting model is under unprecedented strain. The days of “set it and forget it” hosting are over.
Key findings from the AI bot impact report
Bot traffic is dominant, aggressive, and resource-hungry. It targets sites regardless of size, consuming bandwidth and CPU cycles that should be reserved for human customers. The financial and performance costs of ignoring this traffic are rising every year.
What shared hosting users must do next
Review your analytics and server logs. Look for the signs of AI bot exhaustion—slow loads, unexplained spikes, and bandwidth warnings. Acknowledge that shared resources are no longer sufficient for a web populated by AI agents.
Preparing websites for AI-driven traffic
The transition to isolated, performance-driven hosting is the single most effective step you can take to protect your website. By moving to a VPS solution like those offered by Skynethosting.net, you regain control over your resources, protect your SEO rankings, and ensure that when a human customer finally clicks on your site, they are greeted by content, not an error message.



