
How to Choose the Right VPS Plan: A No-Nonsense Technical Guide
TL;DR
- Choosing the right VPS starts with understanding your site type, current traffic, and growth plans so you can size CPU, RAM, and SSD storage correctly without bottlenecks or wasted budget.
- Start small but not underpowered: simple blogs and business sites often work with 1–2 vCPU and 2GB RAM, while eCommerce, apps, and high‑traffic projects usually need multiple cores and 4GB+ RAM.
- Bandwidth, data center location, and storage type matter; NVMe/SSD and nearby data centers reduce latency and keep pages fast even during traffic spikes and media-heavy workloads.
- Choose Linux VPS for most websites to save on licensing and gain stability; pick Windows VPS only if you rely on Microsoft stacks like ASP.NET or SQL Server for your applications.
- Decide between managed and unmanaged VPS: managed plans handle updates, security, and monitoring for you, while unmanaged VPS suits users comfortable managing servers and troubleshooting issues alone.
- Continuously monitor resource usage and performance, then upgrade or adjust plans as traffic and business needs grow instead of locking into an oversized, expensive VPS from day one.
I’ve been in the hosting game for over ten years, and if there’s one thing I’ve learned, it’s that staring at a VPS pricing table can feel like trying to read a foreign language. You’re bombarded with acronyms like vCPU, NVMe, IOPS, and bandwidth limits, all while trying to figure out if spending an extra $10 a month is actually worth it.
Here is the reality: Most people guess. They either buy the cheapest plan and wonder why their site crashes during a traffic spike, or they overpay for resources they’ll never use.
Choosing a Virtual Private Server (VPS) isn’t just about picking a price point; it’s about matching hardware specifications to your specific workload. Whether you are launching a high-traffic eCommerce store, deploying a SaaS application, or just moving away from restrictive shared hosting, understanding the technical specs is the only way to make a smart investment.
In this guide, I’m going to cut through the marketing fluff. We will break down exactly what each specification means, how much power you actually need, and how to avoid the common traps that trip up new VPS owners.
Why Choosing the Right VPS Plan Matters
It might be tempting to just pick a “middle-of-the-road” plan and hope for the best, but the hardware you choose dictates your entire online experience. The wrong choice has real-world consequences.
Performance issues caused by wrong VPS selection
I’ve seen it happen a hundred times. A business owner migrates a heavy WordPress site to a VPS with insufficient RAM or slow disk speeds. The result? The site takes 5 seconds to load. In the world of SEO and user experience, a 5-second load time is a death sentence. If your CPU cores are constantly maxing out, your server will queue requests, leading to timeouts and sluggish performance that frustrates visitors.
Cost implications of over-provisioning
On the flip side, fear often drives people to buy way more power than they need. If you are hosting a static website or a low-traffic blog, paying for 8 dedicated CPU cores and 32GB of RAM is like buying a Ferrari to drive to the grocery store. You are burning budget on resources that sit idle 99% of the time.
Scalability challenges with underpowered servers
The most dangerous scenario is choosing a plan that barely covers your current needs with no room to breathe. A marketing campaign goes viral, or you get a sudden influx of users, and your underpowered server hits a wall. The server crashes exactly when you need it to be most reliable. Choosing the right plan means finding the sweet spot where you have enough headroom to scale without wasting money.
What Technical Specifications Define a VPS Plan?
When you look at a spec sheet, there are four pillars you need to care about: Processing, Memory, Storage, and Network. Let’s translate these into plain English.
CPU cores and vCPU explained
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of your server. In the VPS world, you rarely get a physical CPU chip all to yourself. Instead, you get “vCPUs” or virtual cores. These are slices of a physical processor allocated to your virtual machine. The more complex your application—like processing checkout transactions or running custom scripts—the more CPU power you need.
RAM allocation and performance impact
RAM (Random Access Memory) is your server’s short-term workspace. Every time a visitor loads a page, opens a database connection, or runs a script, it takes up RAM. If you run out of RAM, your server starts using your hard drive as temporary memory (called “swap”), which is significantly slower and will cause your site to crawl.
Storage type and disk I/O importance
This is often overlooked. Storage isn’t just about how many gigabytes of files you can keep; it’s about how fast the server can read and write that data. Disk I/O (Input/Output) speed determines how fast your database can retrieve information. If you have a fast CPU but slow storage, your processor is just waiting around for data to arrive.
Network speed and bandwidth limits
Bandwidth is the volume of data that can be transferred between your server and your users. Network speed (port speed) is how fast that data can travel. Think of bandwidth as the size of the water tank, and network speed as the width of the pipe.
How Much CPU Power Do You Really Need?
This is usually the most expensive part of the bill, so getting it right is crucial.
Difference between shared CPU and dedicated CPU
Most standard VPS plans use “shared” vCPUs. This means you share the physical processor with other neighbors on the server. It’s fine for sporadic traffic because you get “burst” performance when you need it. However, if your neighbor starts mining crypto or running a heavy attack, your performance might dip (this is called the “noisy neighbor” effect).
Dedicated CPU plans guarantee that a specific core is yours and yours alone. You get 100% of that power, 24/7.
CPU requirements for websites vs applications
For a standard WordPress blog or a portfolio site, 1 or 2 shared vCPUs are usually plenty. The server works hard for a millisecond to generate the page, then rests.
However, if you are running a Node.js application, a game server, or a high-volume Magento store, the CPU is under constant load. In these cases, you need 4+ cores, and preferably dedicated ones, to prevent lag.
CPU-intensive workloads explained
If you are doing data processing, video transcoding, or machine learning tasks, a standard VPS won’t cut it. These are “CPU-intensive” workloads. You need to look for “Compute-Optimized” VPS plans specifically designed to handle sustained 100% CPU usage without being throttled by the hosting provider.
How to Choose the Right RAM for Your VPS
RAM is usually the first bottleneck a growing site hits.
RAM usage for CMS platforms like WordPress
WordPress is memory-hungry, especially if you use page builders like Elementor or have lots of plugins. A bare-bones WordPress install might run on 512MB, but it won’t be stable.
- Small WP Site: 2GB RAM is the safe minimum.
- Medium WP Site (WooCommerce): 4GB to 8GB RAM.
- Heavy Traffic: 16GB+ RAM.
RAM requirements for databases
Databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB) love RAM. They try to keep as much data as possible in memory to avoid reading from the slow hard disk. If your database is 1GB in size, having enough RAM to cache a significant portion of that will make your application fly.
What happens when RAM is insufficient
When RAM fills up, the Linux kernel triggers the “OOM Killer” (Out of Memory Killer). It sounds dramatic because it is. The system will forcefully kill processes to save the server. Usually, it kills MySQL or your web server software, causing your site to go offline instantly with a “Database Error Establishing Connection” message.
Why Storage Type Matters in VPS Hosting
Never compromise on storage speed. It is the single biggest factor in “snappy” page loads.
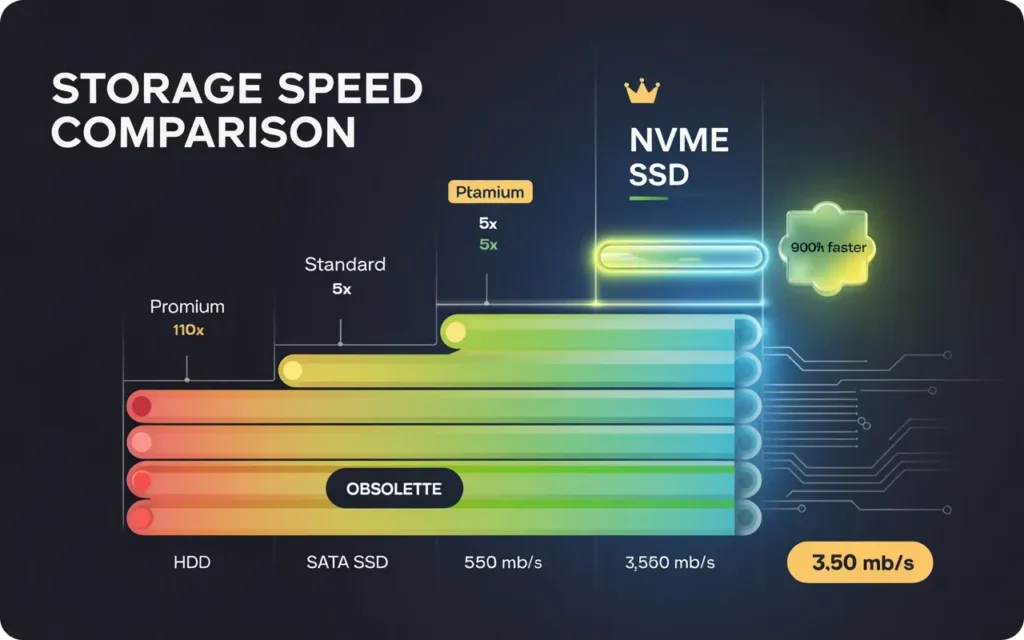
NVMe vs SSD vs HDD performance comparison
- HDD (Spinning Disk): Obsolete for hosting websites. Only use these for cold storage backups.
- SATA SSD: The standard for the last 5 years. Fast, reliable, and affordable.
- NVMe SSD: The new standard. NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) drives are plugged directly into the motherboard via PCIe slots.
Providers like Skynethosting.net utilize NVMe storage because it is drastically faster—up to 900% faster than traditional SATA drives. If you have the choice between a standard SSD VPS and an NVMe VPS, always take the NVMe. The price difference is negligible, but the performance jump is massive.
Disk IOPS and real-world speed impact
IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) measures how many times the hard drive can read or write in a second. High IOPS are critical for eCommerce stores where customers are constantly writing data (adding to cart, checking out) and for forums where databases are constantly updating.
Storage planning for future growth
Storage is the hardest thing to shrink. You can always upgrade to more space, but migrating to a smaller disk later is technically difficult. Start with what you need (e.g., 50GB) but ensure your host allows you to expand storage without rebuilding the entire server.
How Bandwidth and Network Speed Affect Performance
Don’t let a slow connection throttle your fast hardware.
Difference between bandwidth and throughput
Throughput is the speed of the port. Most decent VPS providers offer a 1Gbps (Gigabit) port. This ensures that if 100 people hit your site at once, the pipe is wide enough to serve them all quickly.
Bandwidth is the cap on data transfer (e.g., 5TB per month).
Monthly data transfer limits explained
Most text-based websites will never hit their bandwidth cap. A busy blog might use 100GB a month. However, if you host video, high-res images, or large downloads, you eat through bandwidth quickly. Always check the overage fees. Some hosts shut you down when you hit the limit; others charge you per GB.
Traffic spikes and bandwidth planning
If you expect seasonal spikes (like Black Friday), ensure your network port isn’t capped at 100Mbps. A 100Mbps port can easily get saturated by a modest DDoS attack or a viral social media post, making your site inaccessible even if your CPU is bored.
Managed vs Unmanaged VPS – Which Should You Choose?
This is a decision about your time and skills, not just hardware.
Technical skills required for unmanaged VPS
An unmanaged VPS is a blank slate. You get the operating system, and that’s it. You need to know how to:
- Install a web server (Nginx/Apache).
- Configure firewalls (UFW/IPTables).
- Set up backups.
- Patch security vulnerabilities.
If you aren’t comfortable using the command line (SSH), an unmanaged VPS will be a nightmare.
Benefits of managed VPS hosting
Managed hosting puts the responsibility on the provider. They handle the OS updates, security patches, and often include a control panel (like cPanel or DirectAdmin). If something breaks at 3 AM, it’s their problem, not yours.
Cost vs responsibility comparison
Managed VPS plans cost more because you are paying for human expertise. However, calculate the cost of your time. If you spend 5 hours a month fixing server issues, isn’t that worth the extra $20-$30 for a managed plan?
How Operating System Choice Impacts VPS Specs
The software you run dictates the hardware you need.
Linux VPS resource efficiency
Linux (Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian) is the industry standard for a reason. It is incredibly efficient. A Linux server can run smoothly with no graphical interface, using very little RAM for the system itself.
Windows VPS licensing and RAM usage
Windows Server requires a Graphical User Interface (GUI), which eats up resources. You typically need at least 2GB of extra RAM just to keep the OS running smoothly. Plus, you have to factor in the cost of the Windows license, which usually adds to the monthly fee. Only choose Windows if you specifically need to run .NET applications or ASP.net.
Matching OS to your application stack
Don’t fight the current. If your app is built in PHP/Python/Ruby, Linux is the native home. If you rely on Microsoft SQL Server, go Windows.
How to Match VPS Specifications to Use Cases
Let’s look at some common scenarios so you can identify where you fit.
VPS for websites and blogs
- Focus: RAM and Caching.
- Recommendation: 2-4 vCPU, 4GB RAM, NVMe storage. Focus on setting up server-level caching (like LiteSpeed) to reduce load.
VPS for eCommerce platforms
- Focus: CPU power and IOPS.
- Recommendation: 4+ vCPU, 8GB+ RAM. You need fast database performance (NVMe is mandatory here) to ensure the checkout process is instant. Slow checkouts = abandoned carts.
VPS for developers and testing environments
- Focus: Flexibility.
- Recommendation: A small unmanaged slice (1 vCPU, 2GB RAM) is usually enough to test code. The ability to destroy and rebuild the server instantly is key here.
VPS for SaaS and applications
- Focus: Scalability and Redundancy.
- Recommendation: Start with a robust setup (4 vCPU, 16GB RAM) but ensure the host allows for easy vertical scaling as your user base grows.
How to Scale VPS Resources Without Downtime
The beauty of a VPS is that it isn’t set in stone.
Vertical scaling explained
Vertical scaling means adding more power to an existing server (e.g., upgrading from 4GB to 8GB RAM). Good providers allow you to do this with a simple reboot, taking less than 2 minutes.
When to upgrade CPU or RAM
Monitor your resources. If your RAM usage consistently sits above 80%, it’s time to upgrade. If your “CPU Steal” or load average is high, you need more cores. Don’t wait until it hits 100%.
Planning VPS growth strategically
Start small. There is no need to buy the biggest plan on day one. Pick a provider that makes upgrading easy so you can grow your costs in line with your revenue.
Common VPS Specification Mistakes to Avoid
Choosing cheap VPS without NVMe
I see cheap hosting offers for $2/month using old HDD or cheap SATA SSDs. Avoid them for production sites. The few dollars you save aren’t worth the laggy performance.
Ignoring CPU contention
Be wary of hosts that oversell their servers aggressively. If a host offers absurdly high specs for an incredibly low price, they are likely cramming too many users onto one machine, meaning you’ll never actually get the performance you paid for.
Underestimating RAM requirements
This is the #1 reason for server crashes. People try to run a Magento store on 2GB of RAM. It works for one user, but crashes with five. Always budget for slightly more RAM than you think you need.
Why Skynethosting.net VPS Plans Are Easy to Choose
If you are looking for a balance of power and ease of use, looking at the infrastructure provided by Skynethosting.net makes the choice much simpler.
Clearly defined technical specs
Skynet is transparent about what you get. Whether you need a starter VPS or a high-end corporate server, the RAM, CPU, and bandwidth limits are clearly laid out so you aren’t guessing.
NVMe-powered VPS infrastructure
As mentioned earlier, storage speed is king. Skynet utilizes NVMe storage that is 900% faster than traditional SATA drives. This ensures your applications load instantly and your databases handle queries without choking.
Flexible scaling and expert support
Skynet has been in business for 20 years for a reason. With 24/7 friendly customer service and the ability to resell or scale servers, you have a partner that grows with you. Plus, features like free WHMCS licenses for resellers and LiteSpeed web servers add massive value on top of the raw hardware specs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right VPS plan doesn’t have to be a gamble. By focusing on the core specifications—vCPU type, RAM amount, NVMe storage, and bandwidth—you can build a hosting environment that is fast, reliable, and cost-effective.
Summary of VPS specification selection
- CPU: Go for Dedicated if you have sustained load; Shared is fine for websites.
- RAM: 2GB minimum for modern web apps; 8GB+ for eCommerce.
- Storage: Always choose NVMe.
- Management: If you can’t fix a Linux kernel panic, pay for Managed hosting.
Final checklist before buying a VPS plan
- Does the plan offer NVMe storage?
- Is there enough RAM to support my specific CMS/Application?
- Is the bandwidth sufficient for my expected traffic?
- Can I upgrade this plan easily if I grow next month?
- Does the support team work 24/7 in case of emergencies?
Choosing performance-focused VPS hosting
Your server is the foundation of your digital business. Don’t build on shaky ground. Invest in specs that provide speed and stability, and your users (and Google) will thank you for it.



