What Is a Domain Name? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
TL;DR
- A domain name is a website’s user-friendly address, essential for brand identity, trust, and easy online access.
- Domains build credibility, enhance branding, are memorable, help SEO, and enable custom business email addresses.
- The DNS (Domain Name System) translates domains into computer-friendly IP addresses, making web browsing seamless for users.
- Domain names are categorized by extensions: generic (.com, .org), country code (.uk, .us), newer generic (.online), and subdomains (blog.example.com).
- Domains are just the address; web hosting is necessary to store and serve the actual website files—both work together to put a site online.
- Choosing the right domain means keeping it short, relevant, brand-aligned, and free of confusing characters for best results.
- Registering a domain involves picking a registrar, checking availability, entering details, and renewing regularly—Skynethosting.net offers affordable registration, free privacy protection, bundles, and 24/7 support.
Starting a website can feel like learning a new language, with terms like “domain name,” “hosting,” and “DNS” thrown around. After a decade of helping people build their online presence, I’ve found that the biggest hurdle is often just understanding these basic building blocks. The good news is, it’s much simpler than it sounds.
This guide is designed to walk you through exactly what a domain name is, without any confusing jargon. You’ll learn how domains work, why they’re essential for your brand, and how to choose and register the perfect one for your project. By the end, you’ll have the confidence to take that first crucial step toward establishing your identity on the web.
What Is a Domain Name and Why Is It Important?
Let’s start with the basics. Think of a domain name as your website’s street address. It’s the unique name people type into their browser to find you online.
Simple Definition of a Domain Name
In simple terms, a domain name is the text that identifies a specific website. For example, our domain name is skynethosting.net. Other domain name examples include google.com and wikipedia.org. It’s a human-friendly label that points to a specific location on the internet. Without domain names, we’d be stuck trying to remember long strings of numbers to visit our favorite sites.
How Domains Represent Your Website Online
Your domain name is more than just a technical label; it’s a core part of your online brand identity. It’s often the very first impression someone has of your business or personal project. A good domain name can convey professionalism, build trust, and give people an idea of what you’re all about before they even click on the link. It’s your digital storefront sign, your business card, and your virtual handshake all in one.
Why Businesses and Individuals Need a Domain
The importance of domain names cannot be overstated, whether you’re a global corporation or a solo blogger. Here’s why having your own domain is crucial:
- Credibility and Professionalism: Having a custom domain like
yourbusiness.comlooks far more professional than using a free subdomain likeyourbusiness.wordpress.com. It shows you are serious about your venture. - Brand Ownership: Your domain name is your unique online property. It secures your brand name and prevents others from using it to trade on your reputation.
- Memorability: A short, memorable domain is easy for customers to remember and type, making it simpler for them to return to your site.
- SEO Benefits: A domain name that includes relevant keywords can give you a slight edge in search engine rankings, helping potential customers find you more easily.
- Marketing and Promotion: It serves as the foundation for your marketing efforts. You’ll feature it on social media, in ads, and on physical marketing materials.
- Custom Email Addresses: Owning a domain allows you to create professional email addresses like
contact@yourbusiness.com, which builds trust and reinforces your brand with every message you send.
How Does a Domain Name Work?
Now that you know what a domain is, let’s pull back the curtain and look at the magic that happens when you type one into your browser. The process is a seamless, behind-the-scenes dance between your computer and a global network.
Domain Name vs. IP Address
Every device connected to the internet, including the servers that host websites, has a unique IP (Internet Protocol) address. An IP address is a long string of numbers, like 192.168.1.1. While computers can easily read and remember these numbers, humans can’t.
A domain name is essentially a memorable alias for an IP address. Instead of needing to remember a complex numerical sequence, you just need to remember skynethosting.net. This is where the Domain Name System comes in.
Role of the DNS (Domain Name System)
The Domain Name System (DNS) is often called the “phonebook of the internet.” It’s a massive, distributed database that translates human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. When you enter a domain name into your browser, the DNS is responsible for looking up the corresponding IP address so your browser knows where to find the website’s files. The DNS is what makes the internet user-friendly. Without it, we’d all be carrying around notebooks filled with IP addresses.
How Browsers Use Domains to Access Websites
Here’s a step-by-step look at how it all works together:
- You type a domain name, like
skynethosting.net, into your browser and hit Enter. - Your browser sends a request to the DNS to find the IP address associated with that domain.
- The DNS servers look up the domain name in their records and find the matching IP address.
- The DNS sends this IP address back to your browser.
- Your browser then uses the IP address to connect to the web server where the website’s files are stored.
- The web server sends the website’s data back to your browser, which then displays the webpage on your screen.
This entire process happens in a matter of seconds, creating a smooth experience for the user.
What Are the Different Types of Domain Names?
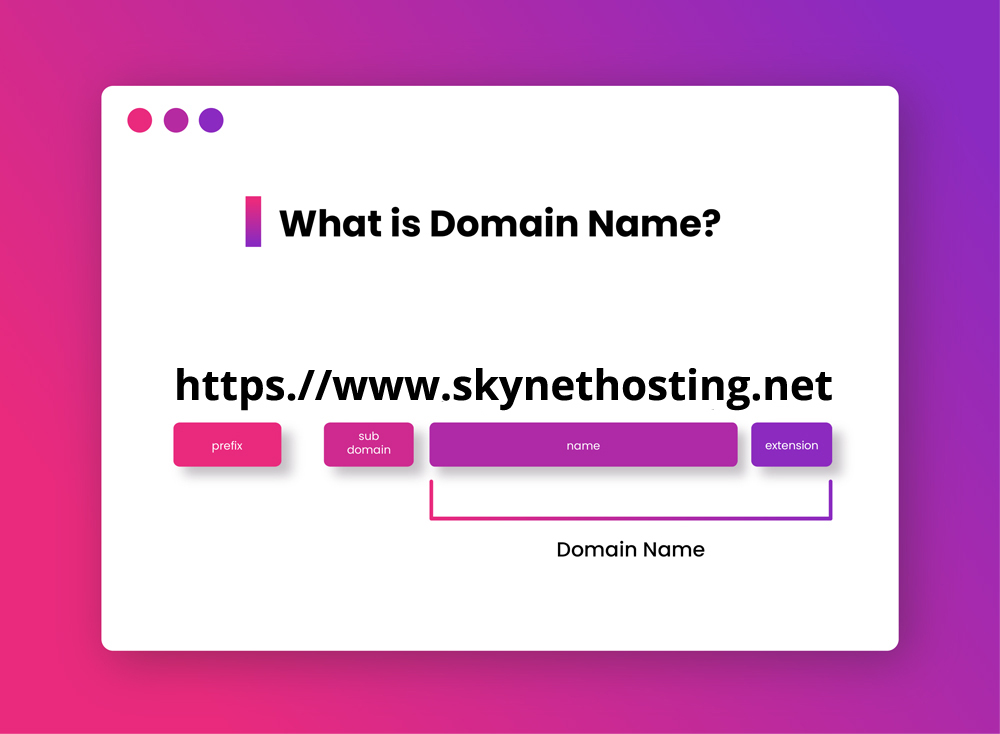
When you register a domain, you’ll notice it’s made of two parts: the name itself (like “skynethosting”) and an extension (like “.net”). This extension is known as a Top-Level Domain (TLD). There are several types of TLDs, each with a different purpose.
Top-Level Domains (TLDs) like .com, .org, .net
These are the most common and recognizable domain extensions. Originally, they had specific purposes:
- .com: For commercial businesses.
- .org: For non-profit organizations.
- .net: For network-related organizations.
Over time, these distinctions have blurred, and now .com is the most popular and sought-after TLD for all types of websites. It’s generally the first choice for businesses aiming for a global or broad audience.
Country-Code TLDs (ccTLDs) like .uk, .lk, .us
Country-Code Top-Level Domains are reserved for specific countries. For example:
- .uk for the United Kingdom
- .lk for Sri Lanka
- .us for the United States
- .ca for Canada
Businesses often use ccTLDs to target audiences in a specific geographic location. Using a local ccTLD can build trust with local customers and may improve your site’s ranking in local search results.
Generic TLDs (gTLDs) like .xyz, .online
In recent years, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), the organization that manages domains, has introduced hundreds of new generic TLDs. These are more descriptive and can help communicate the purpose of a website. Examples include:
- .app
- .blog
- .shop
- .online
- .xyz
These can be a creative way to secure a memorable domain if the .com version is already taken. For instance, a coffee shop might choose yourbrand.coffee.
Subdomains (blog.example.com)
A subdomain is a prefix added to your main (or root) domain. It creates a separate section of your website. For example, in blog.skynethosting.net, “blog” is the subdomain. Subdomains are useful for organizing your site. You might use them for:
- A blog (
blog.yourdomain.com) - An online store (
shop.yourdomain.com) - A support section (
support.yourdomain.com)
Subdomains are free to create if you own the main domain name.
What Is the Difference Between a Domain Name and Web Hosting?
This is one of the most common points of confusion for beginners. While a domain name and web hosting are both essential for a website, they are two separate services.
Domain as Your Website Address
As we’ve discussed, the domain name is your website’s address. It’s what people use to find you. When you buy a domain name, you are reserving that address for your exclusive use for a specific period (usually one year or more).
Hosting as the Home of Your Website Files
Web hosting is the physical space where your website’s files, images, and databases are stored. It’s like the plot of land where you build your house. These files are kept on powerful computers called servers, which are connected to the internet 24/7. When someone visits your domain name, the server sends your website’s files to their browser.
How Both Work Together to Build a Website
Think of it this way:
- The domain name is the address of your house.
- The web hosting is the house itself, where you store all your belongings.
You need both to have a functional website. You register a domain name, purchase a hosting plan, and then connect the two by updating your domain’s DNS records to point to your web host’s servers.
How to Choose the Right Domain Name for Your Website?
Choosing a domain name is a big decision. It will be with you for a long time, so it’s worth putting some thought into it. Here are my top tips after seeing thousands of domains over the years.
Keep It Short, Simple, and Memorable
Long and complicated domains are hard to remember and easy to mistype. Aim for a name that is concise and rolls off the tongue. The best domain names are catchy and stick in people’s minds.
Use Relevant Keywords Carefully
Including a keyword related to your business or niche can be beneficial for SEO. For example, if you’re a photographer in New York, a domain like nyphotostudio.com could be a good choice. However, don’t stuff it with keywords, as that can look spammy (e.g., best-cheap-new-york-photographer.com).
Consider Your Target Audience and Branding
Your domain name should align with your brand. Is your brand playful or professional? Modern or traditional? The name you choose should reflect your brand’s personality. Also, think about your target audience and choose a name that will resonate with them.
Avoid Hyphens, Numbers, and Complex Spellings
Hyphens and numbers can be confusing. When you tell someone your domain name, you’ll have to say “dash” or “the number five.” This creates unnecessary friction. Similarly, using unusual spellings or words that are commonly misspelled (like “expresso” instead of “espresso”) can lead to lost traffic.
How to Register a Domain Name?
Once you have a name in mind, the next step is to register it. The domain registration process is straightforward.
Steps in the Domain Registration Process
- Choose a Domain Registrar: A registrar is a company accredited by ICANN to sell domain names. Skynethosting.net is a registrar, but there are many others.
- Check Domain Availability: Use the registrar’s search tool to see if your desired domain name is available.
- Provide Your Details: You’ll need to provide contact information (name, address, email), which is required by ICANN. This is known as WHOIS information.
- Choose a Registration Period: You can register a domain for a period of one to ten years.
- Complete the Purchase: Pay for the domain, and it’s yours!
Domain Name Availability Check
If your first choice is taken, don’t be discouraged. Try variations, such as adding a verb (e.g., getmybrand.com) or considering a different TLD. Most registrars will suggest alternatives if your initial choice isn’t available.
Renewal and Ownership Details
Remember that you don’t own a domain name forever; you rent it. It’s crucial to keep your contact details updated and renew your domain before it expires. If you let it expire, it could be registered by someone else, and you might lose it for good. Most registrars offer an auto-renewal feature, which I highly recommend enabling.
Why Choose Skynethosting.net for Domain Registration and Hosting?
While you have many options, we’ve designed our services at Skynethosting.net specifically to make this process as simple and affordable as possible, especially for beginners.
Affordable Domain Registration with Hosting Bundles
We believe in providing value. That’s why we offer competitively priced domain registrations and often include a free domain for the first year when you purchase one of our web hosting plans. This bundling saves you money and simplifies management since your domain and hosting are in one place.
Free Add-ons like WHOIS Privacy Protection
When you register a domain, your personal information is publicly listed in the WHOIS database. We offer free WHOIS privacy protection, which replaces your details with our company’s information, protecting you from spam and identity theft.
24/7 Support and Global Reliability
We know that questions can arise at any time. Our friendly support team has been available 24/7 for over 20 years, ready to help you with any issue, whether it’s connecting your domain to your hosting or setting up a custom email address. With data centers in over 25 worldwide locations, we ensure your website is fast and reliable for visitors everywhere.
Your First Step to an Online Presence
Let’s quickly recap. A domain name is your website’s unique address on the internet, a crucial part of your brand identity that makes you look professional and helps customers find you. It works with web hosting to bring your website to life, with the DNS system acting as the translator between human-friendly names and computer-friendly IP addresses.
Choosing the right domain is one of the most important first steps you’ll take. A great domain name is an asset that will serve your brand for years to come. Take your time, follow the tips in this guide, and choose a name that you’re proud to share with the world.
Ready to claim your corner of the internet? Register your domain today with Skynethosting.net and get started on your online journey with a team that has your back every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How much does a domain name cost?
1. How much does a domain name cost?
The cost of a domain name typically ranges from $10 to $20 per year for common extensions like .com. Prices can vary based on the registrar and the popularity of the TLD. Some premium domains can cost thousands of dollars.
Can I change my domain name later?
No, you cannot change a domain name once it is registered. You would need to register a new domain name and then redirect traffic from your old domain to the new one. This is why it’s important to choose carefully from the start.
What is the difference between a URL and a domain name?
A domain name is part of a URL (Uniform Resource Locator). The domain name is the main identifier (e.g., skynethosting.net), while the URL is the full path to a specific page on that site (e.g., https://skynethosting.net/reseller-hosting.htm).
How long can a domain name be?
A domain name can be between 1 and 63 characters long, not including the TLD extension. However, for practical and branding purposes, it’s best to keep it as short and memorable as possible—ideally under 15 characters.
What happens if I forget to renew my domain?
If you forget to renew your domain, it will enter a grace period where you can still renew it (sometimes with an extra fee). If you don’t renew it during this time, it becomes available for others to purchase.
Can I have more than one domain name for my website?
Yes, you can register multiple domain names and have them all point to the same website. This is a common strategy for protecting a brand, capturing common misspellings of a name, or targeting different markets with various TLDs.
What is ICANN?
ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) is a non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the maintenance and procedures of several databases related to the namespaces of the Internet, ensuring the network’s stable and secure operation. They oversee domain registration.



