Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation – How Networks Adapt to Demands
TL;DR
- Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) assigns bandwidth in real time based on actual demand, resulting in much better efficiency than static allocation.
- DBA works through on-demand allocation, fairness, and efficiency, using algorithms to monitor traffic and redistribute unused bandwidth intelligently.
- Algorithms like IPACT, hybrid slot-based schemes, and machine learning approaches are tailored for optical, wireless, and satellite networks to maximize performance.
- Key benefits include increased network utilization, lower latency, better support for real-time traffic (QoS), and reduced costs by maximizing the use of existing infrastructure.
- Challenges include complex algorithm design, potential fairness trade-offs, and the need to plan for network scalability and future growth.
- DBA is vital for adaptive network environments, with proven success in next-gen optical, wireless, and IoT-heavy networks—especially as 5G and cloud adoption grow.
Imagine your home internet slowing to a crawl during peak hours. Or a video call freezing just when you need it most. These frustrations happen because traditional networks can’t adapt to changing demands.
That’s where dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) steps in. It’s the smart technology that makes networks flexible and responsive.
Think of it like a highway system. Static allocation is like having fixed lanes that never change. DBA is like smart traffic management that opens and closes lanes based on real-time traffic flow.
This guide will show you exactly how DBA works. You’ll learn why it matters for modern networks. And you’ll see how it’s transforming everything from fiber optics to wireless systems.
What Is Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation and Why Does It Matter?
Dynamic bandwidth allocation is a network management technique that assigns bandwidth to users based on real-time demand. Instead of giving everyone a fixed amount, it distributes resources where they’re needed most.
Here’s the key difference. Static allocation gives each user a predetermined slice of bandwidth. Whether they use it or not, that slice is reserved. Dynamic allocation shares the total bandwidth pool intelligently.
Static systems work fine when traffic is predictable. But modern networks face bursty, unpredictable demands. IoT devices, video streaming, and cloud applications create traffic spikes that static systems can’t handle efficiently.
DBA systems monitor network traffic continuously. They adjust bandwidth distribution in real-time. When one user needs more capacity, the system can allocate unused bandwidth from other users.
This approach maximizes network utilization. It also improves performance for delay-sensitive applications like voice and video calls.
How Does DBA Work and What Principles Make It Effective?
DBA operates on three fundamental principles: on-demand allocation, fairness, and efficiency.
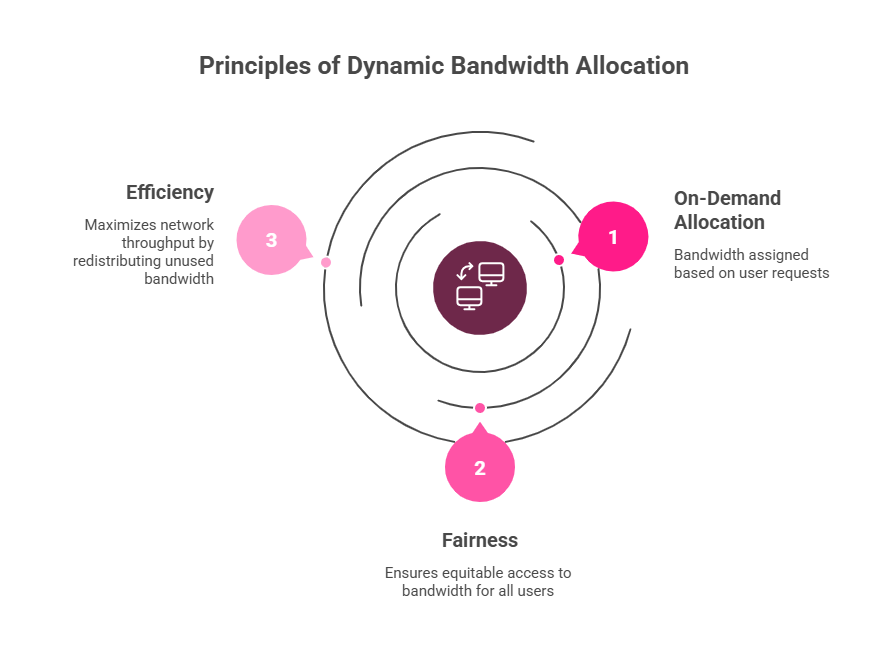
- On-demand allocation means bandwidth is assigned when requested. Users don’t get bandwidth they don’t need. Instead, they get more when they have heavy traffic demands.
- The process starts with bandwidth requests. Network devices send uplink bandwidth requests to a central controller. This controller analyzes current network conditions and allocates resources accordingly.
- Fairness ensures all users get reasonable access to shared bandwidth. DBA algorithms prevent any single user from monopolizing the network. They balance individual needs against overall system performance.
- Efficiency maximizes total network throughput. By redistributing unused bandwidth, DBA systems achieve higher utilization rates than static allocation.
Statistical multiplexing plays a crucial role here. Not all users need maximum bandwidth simultaneously. DBA exploits this statistical pattern to serve more users with the same infrastructure.
The system continuously monitors traffic patterns. It learns from historical data to predict future demands. This traffic-aware bandwidth management enables proactive resource allocation.
Which Algorithms and Protocols Drive DBA Systems?
Several algorithms power DBA systems across different network types.
- IPACT (Interleaved Polling with Adaptive Cycle Time) is widely used in Ethernet Passive Optical Networks (EPON). It polls network terminals in a round-robin fashion. Each terminal reports its bandwidth needs, and IPACT allocates resources based on current demands and fairness policies.
- Guaranteed polling schemes provide minimum bandwidth guarantees while allowing dynamic allocation of excess capacity. These work well for QoS-sensitive applications that need predictable performance.
- Hybrid slot-based schemes combine fixed and dynamic allocation. Critical applications get guaranteed slots, while remaining capacity is distributed dynamically.
- Modern systems increasingly use machine learning for intelligent DBA. Neural network DBA algorithms analyze traffic patterns and predict future demands. This enables more accurate resource allocation, especially in IoT-heavy environments.
- LTE-based dynamic priority allocation methods handle mixed traffic types in mobile networks. They prioritize real-time applications while efficiently managing background data transfers.
Each algorithm has strengths for specific scenarios. IPACT works well for optical networks. Machine learning approaches excel with unpredictable IoT traffic. The key is matching the algorithm to your network’s characteristics.
How Is DBA Applied Across Different Network Types?
DBA implementation varies significantly across network technologies.
- Passive Optical Networks (PON) like EPON and GPON rely heavily on DBA mechanisms. The optical line terminal (OLT) controls bandwidth allocation to optical network units (ONUs). Since PON uses shared upstream channels, DBA is essential for preventing collisions and maximizing efficiency.
- In EPON networks, dynamic polling in optical networks allows the OLT to grant transmission windows based on real-time requests. This prevents bandwidth waste while maintaining fair access.
- WiMAX and wireless broadband systems use DBA for uplink scheduling. The IEEE 802.16e standard includes sophisticated bandwidth request mechanisms. Subscriber stations request bandwidth for different service classes, and the base station allocates resources dynamically.
- VSAT and satellite systems face unique challenges due to long propagation delays. Max-min fairness algorithms ensure equitable bandwidth distribution while accounting for the high latency inherent in satellite communications.
Each network type requires tailored DBA approaches. Optical networks focus on avoiding collisions. Wireless systems must handle mobility and interference. Satellite networks deal with propagation delays and atmospheric conditions.
What Benefits Does Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation Offer?
DBA delivers significant performance improvements over static allocation.
- Increased throughput and utilization is the most obvious benefit. By redistributing unused bandwidth, DBA systems typically achieve 30-50% better utilization than static systems.
- Lower latency and reduced congestion result from more efficient resource allocation. When high-priority traffic needs bandwidth, DBA can provide it immediately rather than forcing it to wait for the next allocation cycle.
- QoS support for delay-sensitive traffic enables better performance for voice and video applications. DBA algorithms can prioritize real-time traffic while ensuring background applications still get adequate resources.
Statistical multiplexing allows networks to support more users with the same infrastructure. Since users rarely need peak bandwidth simultaneously, DBA exploits this statistical pattern to increase overall capacity.
The economic benefits are substantial too. Better utilization means organizations can serve more users without upgrading hardware. This reduces capital expenditure while improving user experience.
What Challenges and Considerations Should You Know About DBA?
Despite its benefits, DBA implementation faces several challenges.
- RTT estimation inaccuracies in optical networks can degrade performance. DBA algorithms rely on accurate round-trip time measurements to synchronize allocation decisions. Errors in RTT estimation lead to suboptimal bandwidth distribution.
- Algorithm complexity increases implementation costs and processing overhead. Sophisticated DBA schemes require powerful controllers and complex software. This can make them impractical for cost-sensitive deployments.
- Fairness vs. performance trade-offs create difficult design decisions. Maximizing total throughput might disadvantage some users. Ensuring perfect fairness might reduce overall system performance.
Resource allocation algorithm design must balance multiple competing objectives. Real-world networks serve diverse applications with different requirements. Finding optimal allocation policies that satisfy all stakeholders is challenging.
Network engineers must also consider scalability. DBA systems that work well with hundreds of users might struggle with thousands. Planning for future growth is essential.
How Is Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation Used in Real-World Applications and Case Studies?
DBA is already transforming network performance across industries.
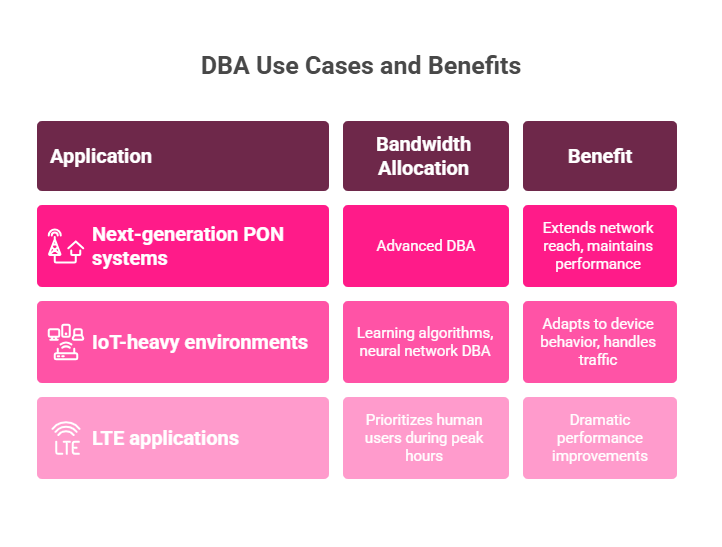
- Next-generation PON systems use advanced DBA for long-reach metro networks. These systems extend optical network reach while maintaining high performance through intelligent bandwidth management.
- IoT-heavy environments benefit from learning algorithms that adapt to device behavior patterns. Smart cities with thousands of sensors use neural network DBA to handle unpredictable traffic bursts efficiently.
- LTE applications handling mixed machine-type communication (MTC) and human-type communication (HTC) traffic show dramatic performance improvements. DBA algorithms prioritize human users during peak hours while ensuring IoT devices maintain connectivity.
Service providers report significant improvements after DBA deployment. One major telecom saw 40% better bandwidth utilization in their PON networks. Another reduced customer complaints about slow speeds by 60% after implementing intelligent DBA in their wireless systems.
These success stories demonstrate DBA’s real-world impact. The technology isn’t just theoretical – it’s delivering measurable benefits today.
Have Questions About DBA? Here Are the Answers
What is Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA)?
DBA is a network method that dynamically assigns bandwidth among users based on current traffic demands, enhancing overall network efficiency and performance compared to fixed, static allocation systems.
How does DBA work?
What are the key algorithms powering DBA?
What advantages does DBA offer over static allocation?
What challenges are faced with DBA?
How is DBA applied in different networks?
DBA is used in passive optical networks (PON), wireless networks like WiMAX, and satellite systems. Approaches are customized: for optical to prevent collision, for wireless to manage mobility, and for satellite to accommodate latency.
What Does the Future Look Like for Adaptive Networks?
Dynamic bandwidth allocation represents a fundamental shift in network design. Instead of rigid, predetermined resource allocation, networks are becoming intelligent and adaptive.
The benefits are clear: better utilization, improved performance, and lower costs. The challenges are manageable with proper planning and algorithm selection.
As networks become more complex and traffic patterns more unpredictable, DBA will become essential. IoT growth, 5G deployment, and cloud adoption all favor dynamic over static allocation.
Start evaluating DBA for your networks now. The technology is mature, proven, and ready for deployment. Your users will notice the difference – and your utilization metrics will too.



