
ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR – Causes, Fixes, and Troubleshooting Guide
TL;DR
- ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR occurs when your browser can’t establish a secure connection to a website, usually because of expired or invalid SSL certificates, or server misconfiguration.
- Common user-side fixes include clearing browser cache, checking system date/time, disabling extensions, or switching browsers.
- Website owners should ensure properly installed and valid SSL certificates, support for modern TLS versions, and correct server settings to prevent errors.
- On mobile devices, clearing app/browser cache, updating the OS or browser, and using public DNS servers can help fix SSL protocol errors.
- Prevent issues with automated SSL tools like Let’s Encrypt, regular SSL health monitoring, and configuring servers to support only secure TLS versions.
- Professional hosting support is recommended for complex cases, especially with certificate chains or server configuration problems.
Have you ever clicked on a website only to see “ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR” staring back at you? You’re not alone. This frustrating error blocks millions of users daily from accessing websites they need.
SSL protocol errors happen when your browser can’t establish a secure connection with a website’s server. The good news? Most of these issues have simple fixes that don’t require technical expertise.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know about SSL protocol errors. You’ll learn what causes them, how to fix them quickly, and how to prevent them from happening again. Whether you’re a website owner or just trying to browse the web, we’ve got you covered.
What Is an SSL Protocol Error?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It’s the technology that creates encrypted connections between your browser and websites. When you see “https://” in your address bar, SSL is working behind the scenes.
The SSL TLS handshake process happens every time you visit a secure website. Your browser and the server exchange certificates and encryption keys. This entire process takes just milliseconds when everything works correctly.
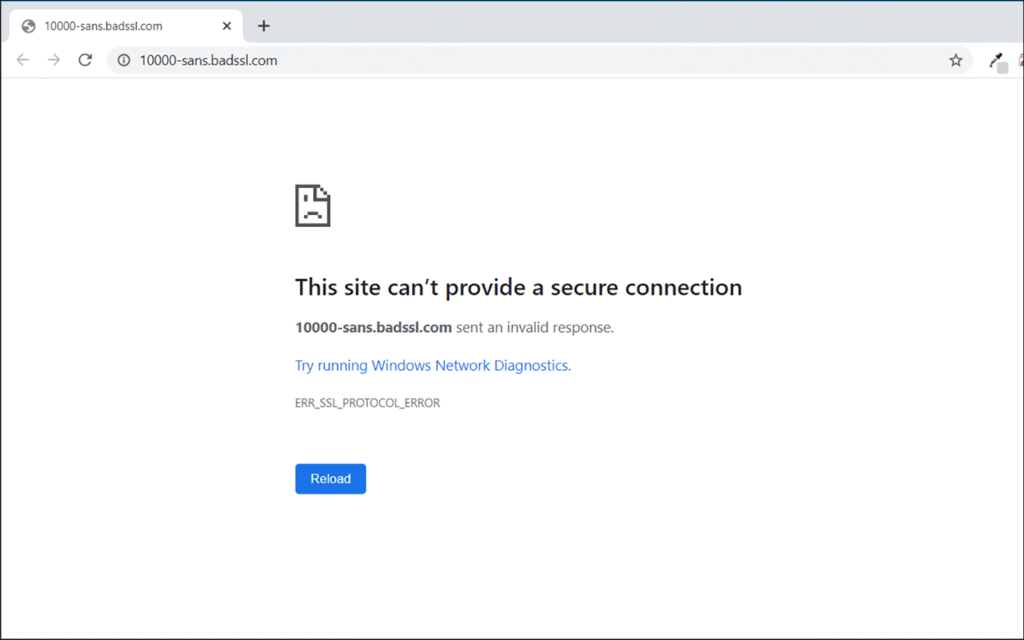
But sometimes things go wrong. When the error occurs, you’ll see messages like “This site can’t provide a secure connection” or “ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR in Chrome.”
This error appears across different platforms. You might see it in Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or on Android devices. The message varies slightly, but the underlying problem remains the same.
Your browser is telling you it cannot establish a secure connection with the website. This breaks the secure protocol that protects your data during transmission.
What Causes the SSL Protocol Error?
Several factors can trigger SSL protocol errors. Understanding these causes helps you fix them faster.
Invalid or Expired SSL Certificates
Websites need valid SSL certificates to create secure connections. When certificates expire or become invalid, browsers reject the connection. Many website owners forget to renew their certificates on time.
TLS Version Incompatibility
Different TLS versions don’t always play well together. Older websites might only support outdated TLS versions. Modern browsers prefer newer, more secure versions. This mismatch causes connection failures.
Firewall and Antivirus Interference
Your antivirus software might block SSL connections it considers suspicious. Corporate firewalls often interfere with encrypted traffic. These security measures sometimes work too well, blocking legitimate connections.
Browser Cache and Cookie Issues
Corrupted browser cache can store incorrect SSL information. Old cookies might contain outdated security data. Browser extensions can also interfere with SSL connections.
Incorrect Date and Time Settings
SSL certificates have specific validity periods. If your device shows the wrong date or time, certificates appear expired or invalid. This confuses the SSL validation process.
Server Configuration Problems
Web servers need proper SSL configuration. Missing certificate chains, incorrect redirect rules, or server downtime can all trigger protocol errors.
How to Fix SSL Protocol Error in Chrome and Other Browsers
Let’s start with the quickest fixes you can try right now.
Clear Browser Cache and SSL State
Your browser cache might contain corrupted SSL data. Clearing it often resolves the issue immediately.
In Chrome, press Ctrl+Shift+Delete (or Cmd+Shift+Delete on Mac). Select “All time” and check all boxes. Click “Clear data.”
Don’t forget to clear SSL state too. On Windows, go to Internet Options > Content > Clear SSL state. This removes stored certificate information.
Disable Browser Extensions
Some extensions interfere with SSL connections. VPN extensions, ad blockers, and security tools are common culprits.
Try browsing in Incognito mode first. If the site loads properly, an extension is likely causing the problem. Disable extensions one by one to find the troublemaker.
Check Your Date and Time Settings
Incorrect date and time settings cause SSL validation failures. Right-click your system clock and select “Adjust date/time.”
Enable automatic time synchronization. This ensures your device stays in sync with internet time servers.
Try a Different Browser
If Chrome shows the error, try Firefox or Safari. Different browsers handle SSL differently. This quick test helps identify browser-specific issues.
Reset Network Settings
Network configuration problems can interfere with SSL connections. On Windows, open Command Prompt as administrator and run:
- ipconfig /flushdns
- netsh winsock reset
- netsh int ip reset
Restart your computer after running these commands.
Fixing SSL Protocol Error on Website/Server Side
Website owners face different challenges when dealing with SSL errors.
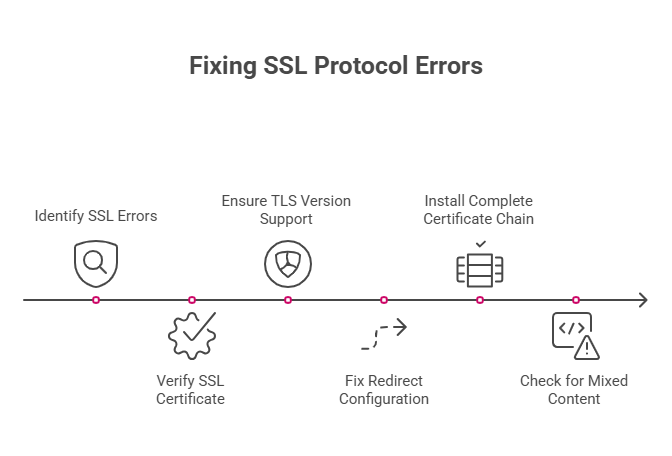
Verify Your SSL Certificate
Check if your SSL certificate is valid and properly installed. Use an SSL checker tool like SSL Labs’ free tester. Enter your domain and wait for the analysis.
Look for expired certificates, missing intermediate certificates, or configuration errors. The certificate authority should have issued a valid certificate that browsers trust.
Ensure Proper TLS Version Support
Modern websites should support TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 at minimum. Older TLS versions have security vulnerabilities and compatibility issues.
Check your server configuration. Disable outdated protocols like SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0. Most hosting providers offer easy ways to update these settings.
Fix Redirect Configuration
Incorrect .htaccess rules or Nginx configurations can create redirect loops. These confuse browsers during the SSL handshake process.
Review your redirect rules. Ensure HTTP traffic redirects to HTTPS cleanly without creating infinite loops.
Install Complete Certificate Chain
SSL certificates often require intermediate certificates. Missing chain certificates cause validation failures in some browsers.
Your certificate authority provides the complete certificate chain. Install all certificates in the correct order on your server.
Check for Mixed Content
Websites serving both HTTP and HTTPS content trigger security warnings. All resources (images, scripts, stylesheets) should load over HTTPS.
Scan your website for mixed content issues. Update all internal links to use HTTPS URLs.
SSL Protocol Error on Android or Mobile Devices
Mobile devices present unique SSL challenges.
Use Chrome’s Mobile Diagnostics
Chrome for Android includes built-in network diagnostics. Open Chrome settings and navigate to “Site settings” > “All sites.” Clear data for problematic websites.
Clear App Cache and SSL State
Android apps store SSL certificates independently. Clear cache and data for affected apps through Settings > Apps.
Verify Mobile DNS Settings
Public DNS servers often resolve SSL issues on mobile networks. Try switching to Google DNS (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1).
Update Your Browser and Operating System
Outdated mobile browsers lack support for modern SSL protocols. Keep your browser and operating system updated to the latest versions.
SSL Protocol Error in WordPress or cPanel Sites
WordPress sites have specific SSL considerations.
Use HTTPS Plugins
WordPress plugins like “Really Simple SSL” automatically fix common HTTPS issues. They update database URLs and fix mixed content problems.
Update Database URLs
WordPress stores URLs in its database. After installing SSL, update these URLs to use HTTPS. Use WordPress CLI or phpMyAdmin for database updates.
Enable AutoSSL in cPanel
cPanel hosting often includes AutoSSL through Let’s Encrypt. This automatically installs and renews SSL certificates for your domains.
Avoid Cloudflare Full SSL with Self-Signed Certificates
Cloudflare’s “Full SSL” mode requires valid certificates on your origin server. Don’t use self-signed certificates in production environments.
How to Prevent SSL Protocol Errors in the Future
Prevention saves time and frustration later.
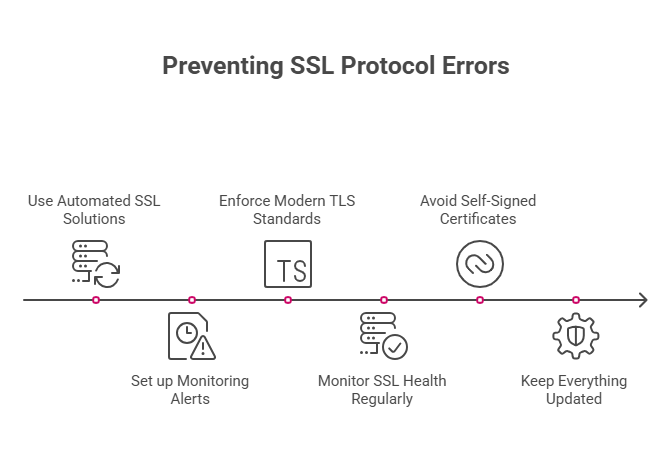
Use Automated SSL Solutions
Let’s Encrypt provides free SSL certificates with automatic renewal. Premium SSL providers also offer auto-renewal features.
Set up monitoring alerts before certificates expire. Most providers send email notifications 30 days before expiration.
Enforce Modern TLS Standards
Configure your server to support only TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3. Disable older, insecure protocols completely.
Monitor SSL Health Regularly
Use SSL monitoring tools to check certificate status weekly. Services like SSL Labs or Qualys provide automated monitoring.
Avoid Self-Signed Certificates in Production
Self-signed certificates trigger browser warnings and compatibility issues. Use certificates from trusted certificate authorities instead.
Keep Everything Updated
Regularly update your web server, browser, and operating system. Security patches often include SSL/TLS improvements.
FAQs – SSL Protocol Errors Explained
What’s the difference between SSL handshake and SSL protocol errors?
SSL handshake errors occur during the initial connection setup. SSL protocol errors happen when the entire SSL system fails to work properly. Both prevent secure connections but at different stages.
Does this error affect SEO?
Yes. Search engines prefer HTTPS websites. SSL errors can hurt your search rankings and user experience. Fix them promptly to maintain good SEO performance.
Can users bypass this error safely?
Users can sometimes proceed past SSL warnings, but it’s not recommended. Bypassing SSL errors exposes personal data to potential interception. Only proceed if you completely trust the website.
Should I reinstall my SSL certificate?
Try other fixes first. If issues with your SSL certificate persist after troubleshooting, reinstalling might help. Contact your hosting provider for assistance with certificate installation.
When to Contact Professional Support
Some SSL issues require expert help.
Contact your hosting provider when basic troubleshooting fails. They can check server logs, reinstall certificates, and analyze redirect chains.
If you use services like SkyNetHosting, their support team can reissue certificates and fix server-side configuration problems.
Professional help becomes necessary when dealing with complex certificate chain issues or advanced server configurations.
Secure Your Connection Today
SSL protocol errors might seem intimidating, but most have straightforward solutions. Start with simple fixes like clearing your browser cache and checking date and time settings.
Website owners should prioritize SSL certificate maintenance and server configuration. Regular monitoring prevents most issues before they affect users.
Remember that internet security depends on working SSL connections. Take time to fix these errors properly rather than ignoring them.
Need immediate help? Try temporarily disabling antivirus software or browser extensions. These quick steps resolve many SSL problems within minutes.
Your secure browsing experience is worth the effort to configure everything correctly.
FAQs
What does ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR mean?
ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR means your browser can’t establish a secure connection to a website, often due to expired or invalid SSL certificates, server misconfiguration, incompatible TLS versions, or problems with your network, browser cache, extensions, or device date and time settings.
What are common causes of SSL protocol errors?
How can users fix SSL protocol errors in browsers?
What should website owners do to fix SSL protocol errors?
Website owners must ensure a valid SSL certificate is properly installed and not expired, enable modern TLS versions, fix redirect configuration, install the complete certificate chain, and verify all resources are served over HTTPS to avoid mixed content errors.
How can mobile users address SSL protocol errors?
What’s the difference between SSL handshake and SSL protocol errors?
How can these errors be prevented in the future?
To prevent SSL protocol errors, automate SSL certificate renewal, enforce modern TLS standards, regularly monitor SSL health, avoid self-signed certificates in production, keep servers and browsers updated, and act promptly when you receive expiry notifications from certificate authorities.


